How to Solve an Exponential Equation: Video Lesson
How to Solve an Exponential Equation
To solve an exponential equation, take logs of both sides of the equation and bring the power down in front of the log. The resulting linear equation can be solved for x. For example, solve 5x=13. Taking logs, log(5x)=log(13). Then xlog(5)=log(13). Now solving for x, x = log(13)/log(5). Therefore, x≈1.59.Solving an Exponential Equation: Example 1
Solve 5x = 13.
Step 1. Take logs of both sides
5x = 13 becomes log(5x) = log(13).
Step 2. Bring down the power in front of the log
The power of x can be written in front of the log so that log(5x) = log(13) becomes xlog(5) = log(13).
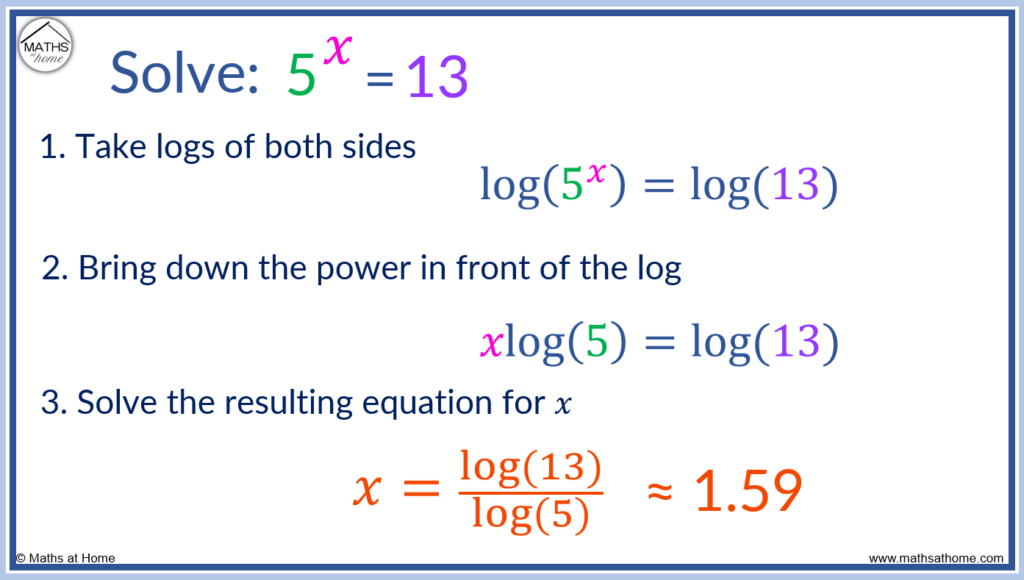
Step 3. Solve the resulting equation for x
xlog(5) = log(13) can be solved for x by dividing both sides of the equation by log(5).
This can be evaluated on a calculator to get 𝑥 ≈ 1.59.
Solving an Exponential Equation: Example 2
Solve 32x = 0.51
Step 1. Take logs of both sides
32x = 0.51 becomes log(32x) = log(0.51).
Step 2. Bring down the power in front of the log
The power of 2x can be written in front of the log so that log(32x) = log(0.51) becomes 2xlog(3) = log(0.51).
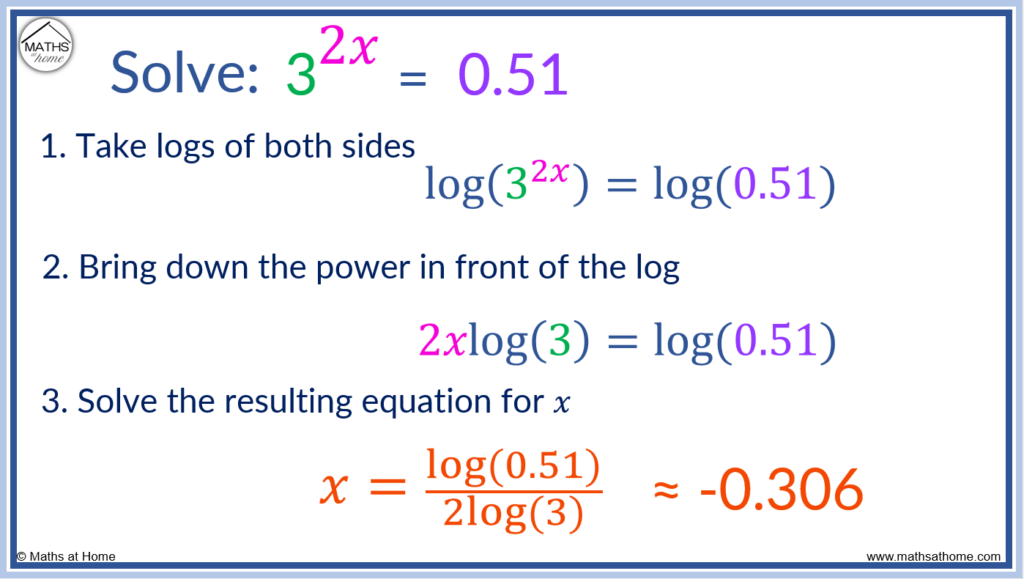
Step 3. Solve the resulting equation for x
2xlog(3) = log(0.51) can be solved by dividing both sides by 2log(3).
This can be evaluated as 𝑥 ≈ -0.306.
How to Solve Exponential Equations with Different Bases
To solve an exponential equation with different bases:
- Take logarithms of both sides of the equation.
- Bring down the exponent in front of the logs.
- Expand and collect x terms.
- Factorise and solve for x.

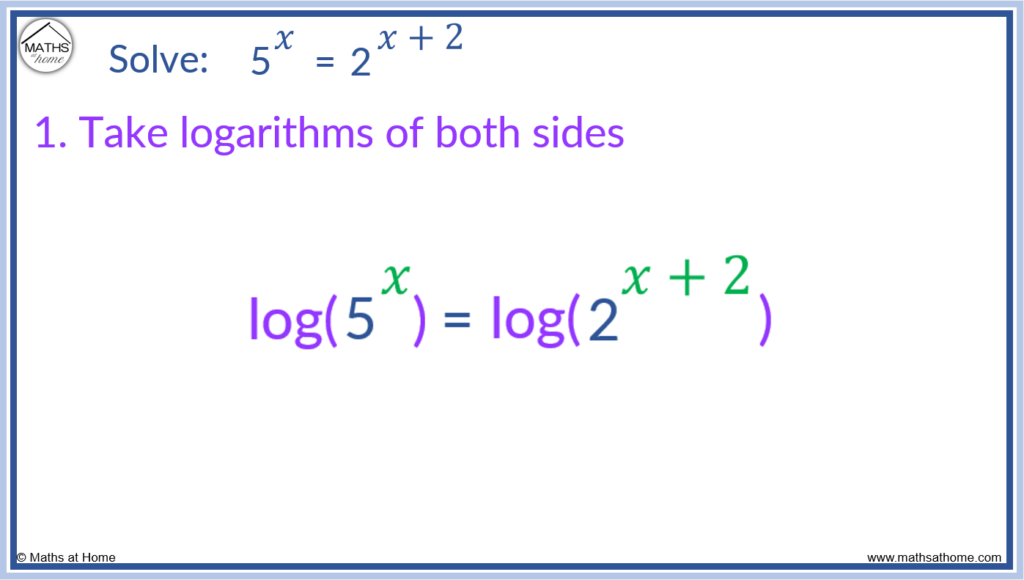
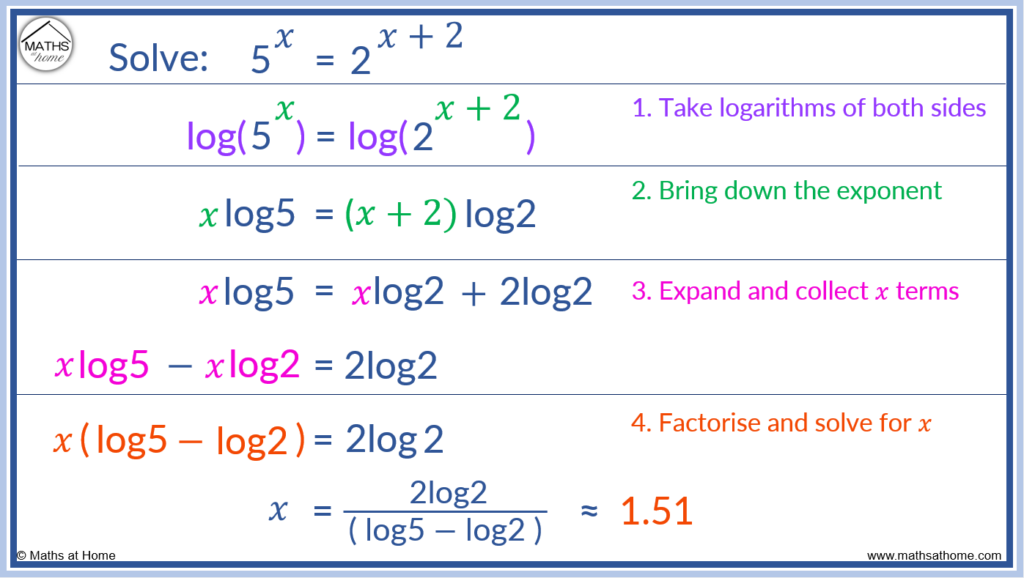
For example solve the exponential equation 5𝑥 = 2𝑥+2.
Step 1. Take logarithms of both sides
Write each side of the equation inside a log.
5𝑥 = 2𝑥+2 becomes log(5𝑥) = log(2𝑥+2).
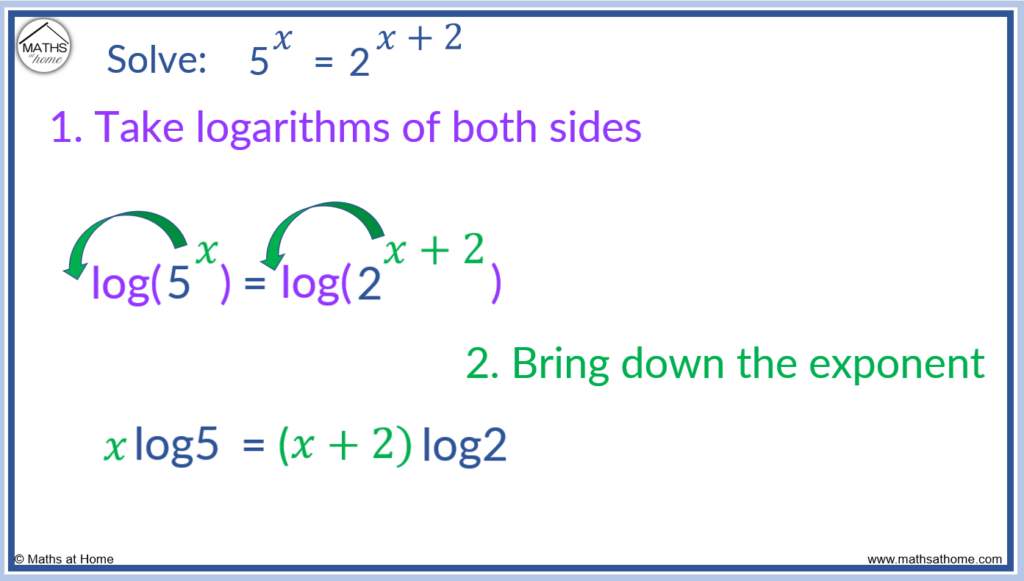
Step 2. Bring down the exponent in front of the logs
Use the log law log(ab) = blog(a) to bring the powers down in front of the logs on both sides.
log(5𝑥) = log(2𝑥+2) becomes 𝑥log(5) = (𝑥+2)log2.
Step 3. Expand and collect 𝑥 terms
Expanding the bracket on the right hand side of the equation, (𝑥+2)log2 becomes 𝑥log2 +2log2.
Now the bracket is expanded, the equation becomes 𝑥log5 = 𝑥log2 + 2log.
We need to gather the 𝑥 terms all together on one side of the equation. We subtract 𝑥log2 from both sides of the equation which gives us:
𝑥log5 – 𝑥log2 = 2log2.

Step 4. Factorise and solve for 𝑥
Now the 𝑥 terms are on one side of the equation, we can factorise 𝑥 out.
𝑥log5 – 𝑥log2 becomes 𝑥(log5 – log2).
Therefore the equation becomes 𝑥(log5-log2) = 2log2.
To solve for 𝑥, we simply divide both sides of the equation by (log5-log2).
Therefore .
This is the exact answer but it can be evaluated on a calculator as 𝑥 ≈ 1.51.
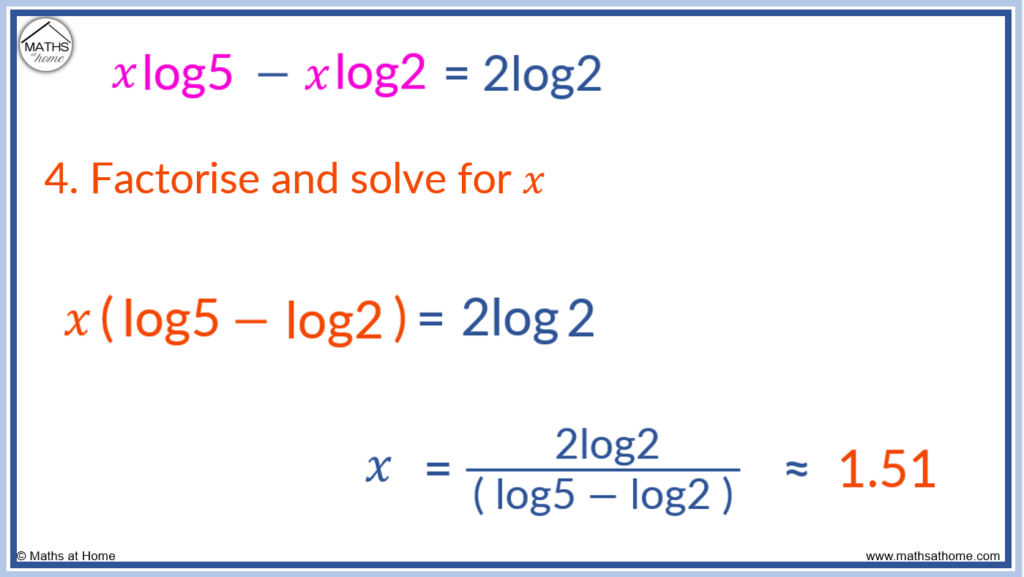
The image below shows a summary of how to solve the exponential equation in steps.
Solving Exponential Equations with e
To solve an exponential equation that has a base of e, take the natural logarithm of both sides of the equation. Then solve the resulting equation for x. For example, solve e2x=5. Taking the natural logarithm of both sides, 2x = ln(5). Dividing both sides by 2, x = ln(5)/2, which approximately equals 0.805.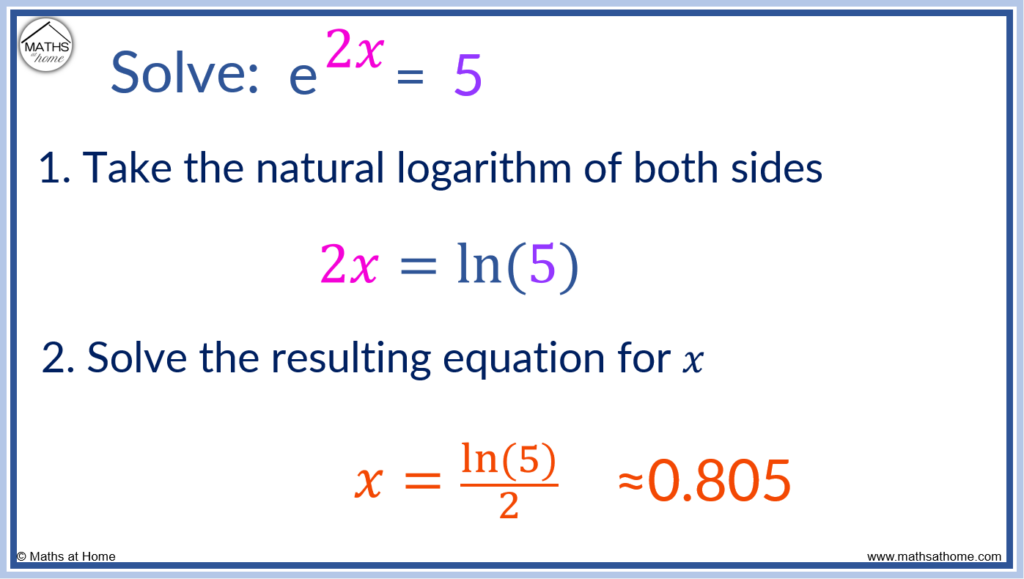
The natural logarithm, ln(x) is the inverse function to ex.
Therefore ln(ex) = x.
In this example, e2x = 5.
Taking the natural logarithm of both sides, we get:
ln(e2x) = ln(5)
Here, ln and e cancel out so that:
2x = ln(5)
Now we solve the resulting equation for x by dividing both sides by 2.
x = ln(5)/2
This is the exact answer and evaluating it on a calculator, we get x ≈ 0.805.
Here is another example.
Solve the exponential equation 5e3x = 31.
When solving exponential equations with e, the natural logarithm ln(x) is used.
However it is important to first remove any coefficients from in front of the e.
We first divide both sides by 5 to get:
e3x = 6.2
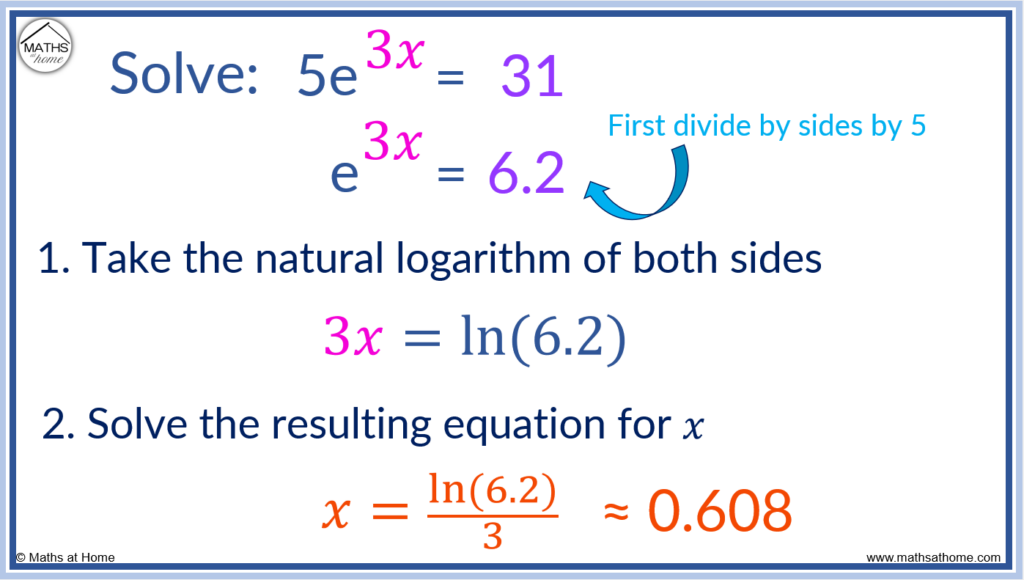
Now the coefficient has been removed, the natural logarithm can be taken.
3x = ln(6.2)
Now we can solve for x by dividing both sides by 3.
x = ln(6.2)/3
Evaluating this on a calculator 𝑥 ≈ 0.608.
How to Solve Exponential Equation with the Same Base
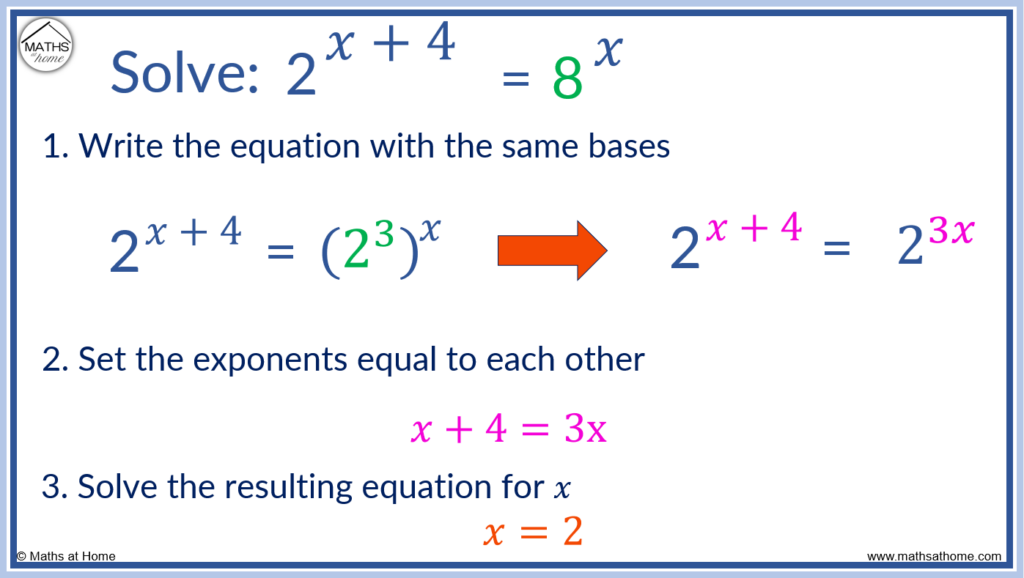
If an exponential equation can be written so that both bases are the same, the equation can be solved by comparing the exponents. For example, 2x+4=8x can be written as 2x+4=(23)x. Expanding, this becomes 2x+4=23x. Setting the exponents equal to each other, x+4=3x and so x = 2.
Solving Exponential Equations with the Same Base: Example 1
In this example, 8 is a power of 2 and so, it is possible to write both sides of the equation with the same base of 2.
Solving Exponential Equations with the Same Base: Example 2
Solve 52x = 51-x
In this example, the bases are already equal. The bases are both 5.
Therefore the exponents must be equal to each other.
2x = 1 – x
Solve this equation for x by adding x to both sides.
3x = 1
Solve for x by dividing both sides of the equation by 3.
x = 1/3
Solving Exponential Equations with the Same Base: Example 3
Solve .
Firstly, write both sides of the equation with the same base.
We can use 9 = 32 and √3 = 31/2 to help us.
Now expanding, this becomes:
Now the bases are equal, the exponents must be equal.
4𝑥 – 2 = 0.5
Now we solve for 𝑥. We add 2 to both sides:
4𝑥 = 2.5
Now we divide by 4 to get:
𝑥 = 0.625
How to Solve Exponential Equations with Fractional Bases
To solve exponential equations with fractional bases:
- Find a common base.
- Equate the exponents.
Solving an Exponential Equation with a Fractional Base: Example 1
Solve
Step 1. Find a common base
Comparing both sides of the equation, 4 and 8 are both powers of 2.
and
.
8 = 23.
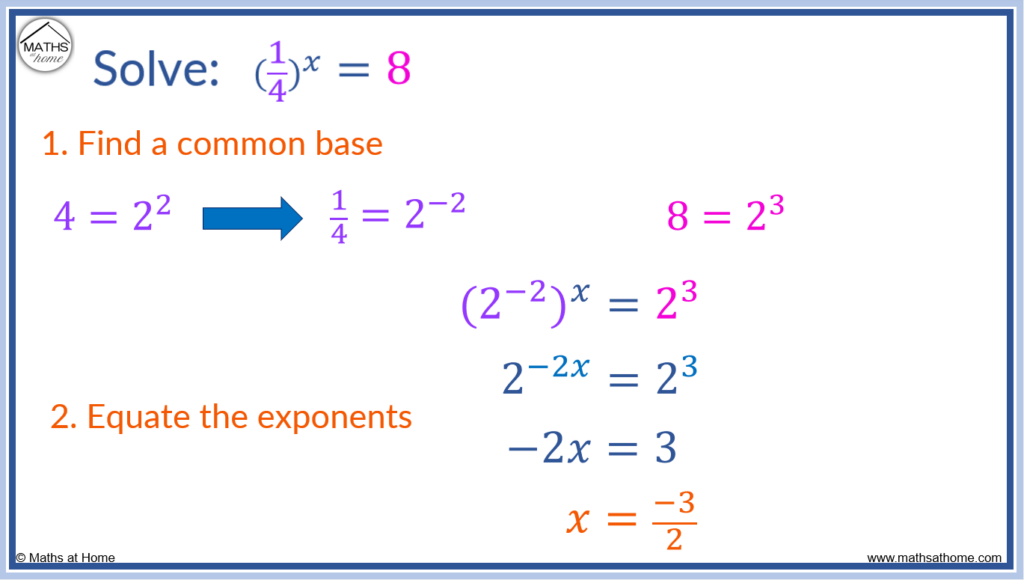
becomes
Step 2. Equate the exponents
Now that the bases are equal, the exponents can be equated.
-2𝑥 = 3
This can be solved for 𝑥 by dividing both sides by -2.
Solving an Exponential Equation with a Fractional Base: Example 2
Solve
Step 1. Find a common base
In this example, we can compare the fractions on each base.
8 = 23 and 27 = 33.
Therefore .
Therefore can be written as
.
This simplifies to.
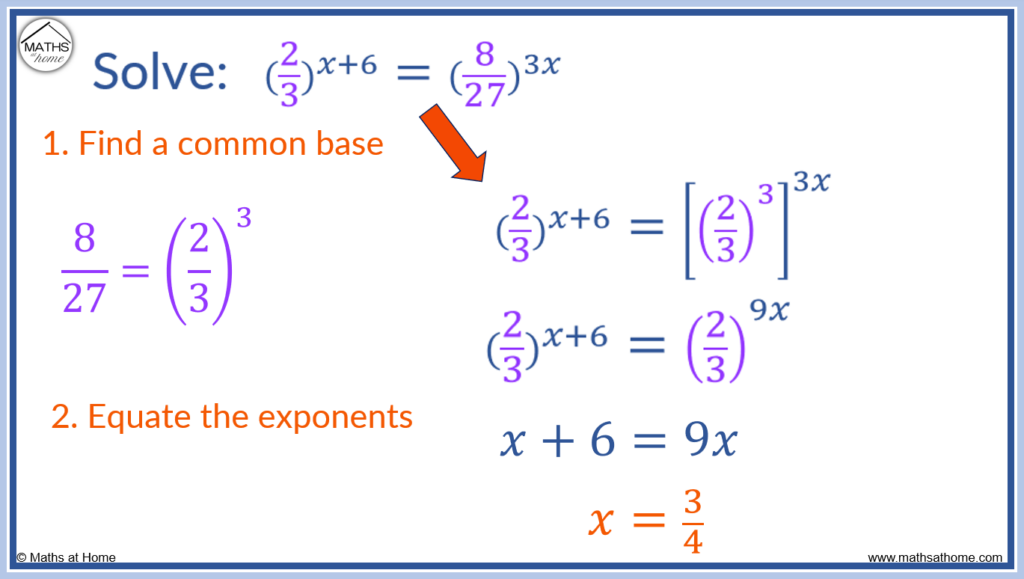
Step 2. Equate the exponents
Now that the bases are the same, the exponents can be equated.
𝑥 + 6 = 9𝑥
This equation can be solved by first subtracting 𝑥 from both sides to get 6 = 8𝑥.
Solving for 𝑥, the solution is .
Solving an Exponential Equation with a Fractional Base: Example 3
For exponential equations involving fractions, where no common base can be found, take logarithms of both sides. Then bring down the power in front of the log and solve for 𝑥.
Solve
Step 1. Take logs of both sides
Step 2. Bring down the power in front of the log
Step 3. Solve for 𝑥
Evaluating this on a calculator, 𝑥 = -5.57.
How to Solve Exponential Equations Involving Quadratics
An exponential equation will lead to a quadratic equation if one base is the square of the other base. For example the equation 9x-5(3x)+6=0 can be written as (3x)2-5(3x)+6=0. Substituting k=3x, this leads to the quadratic equation k2-5k+6=0. This quadratic equation can be solved to find x.
The steps for solving an exponential equation involving a quadratic are:
- Write one base as the other base squared
- Substitute this base for k to form a quadratic
- Solve the resulting quadratic for k
- Solve the exponential equation for x
Solving an Exponential Equation Leading to a Quadratic: Example 1
For example solve .
We know that this equation will lead to a quadratic because 9x is the square of 3x.
Step 1. Write one base as the other base squared
9x = (32)x which can be written as (3x)2.
Therefore 9x = (3x)2.
Therefore can be written as
.
Step 2. Substitute this base for k to form a quadratic
We can substitute k = 3x in the equation so that the quadratic equation of
is formed.
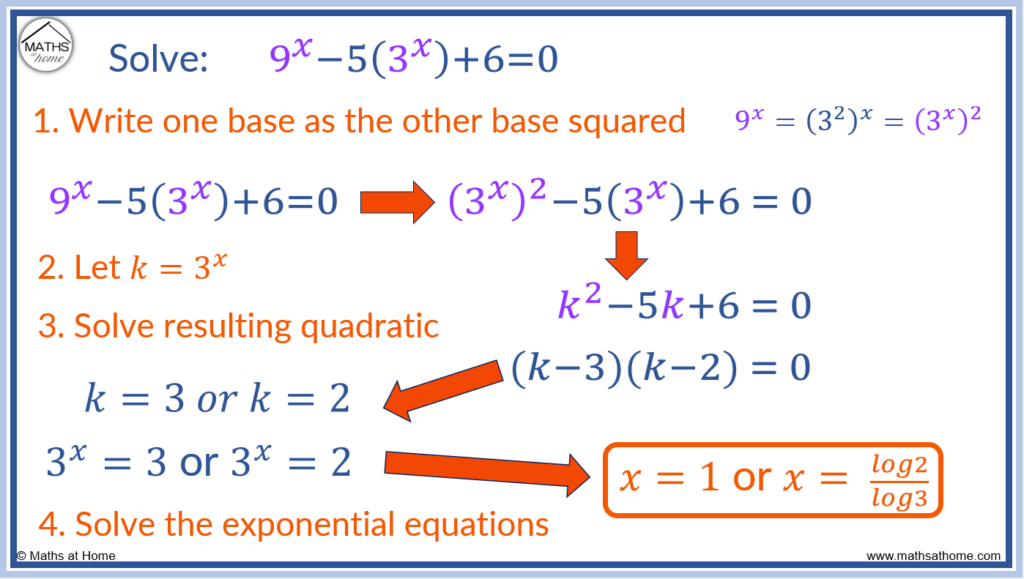
Step 3. Solve the resulting quadratic for k
can be factorised to give (k-3)(k-2) = 0.
Therefore k = 3 or k = 2.
Step 4. Solve the exponential equations for x
Since we set k = 3x, if k = 3 or k = 2 then 3x = 3 or 3x = 2.
If 3x = 3 then x = 1.
If 3x = 2 then we can solve this exponential equation with logs.
log(3x)=log(2) and so, xlog(3) = log(2).
Therefore .
Evaluating this, .
Solving an Exponential Equation Leading to a Quadratic: Example 2
Solve .
Step 1. Write one base as the other squared
25x = (5x)2
Therefore becomes
.
We can write as
.
Step 2. Substitute this base for k to form a quadratic
Let k = 5x so that can be written as
.
Step 3. Solve the resulting quadratic for k
can be written as (k – 4)(k – 1) = 0.
Therefore k = 4 or k = 1.
Step 4. Solve the exponential equations for x
Since k = 5x, the solutions of k = 4 and k = 1 become 5x = 4 and 5x = 1.
If 5x = 4,
If 5x = 1, 𝑥 = 0
