How to Use the Chain Rule Video Lesson
The Chain Rule with Trigonometric Functions
What is the Chain Rule?
The chain rule is used to calculate the derivative of a composite function. The chain rule formula states that dy/dx = dy/du × du/dx. In words, differentiate the outer function while keeping the inner function the same then multiply this by the derivative of the inner function.
The Chain Rule: Leibniz Notation
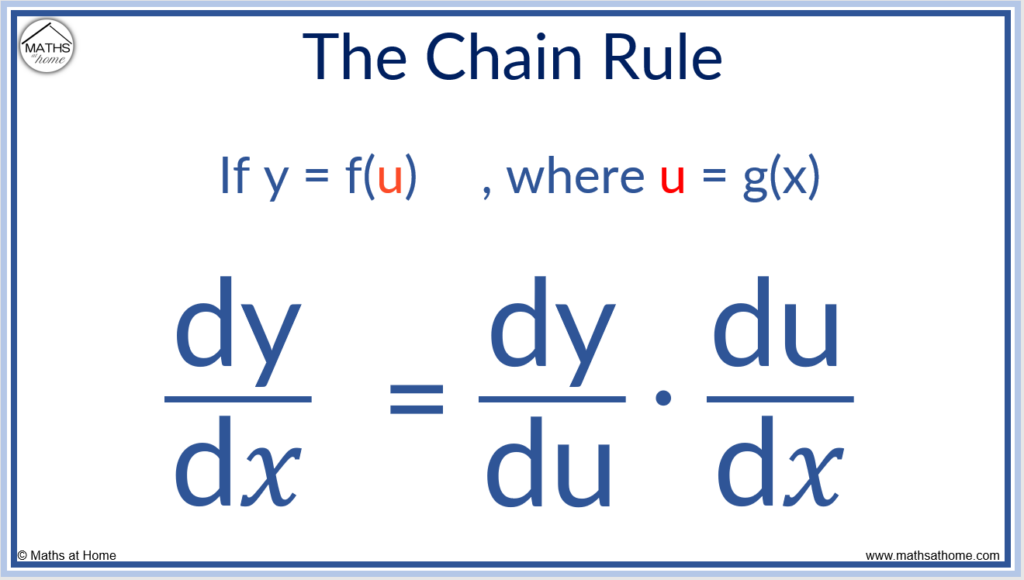
The Chain Rule: Function Notation
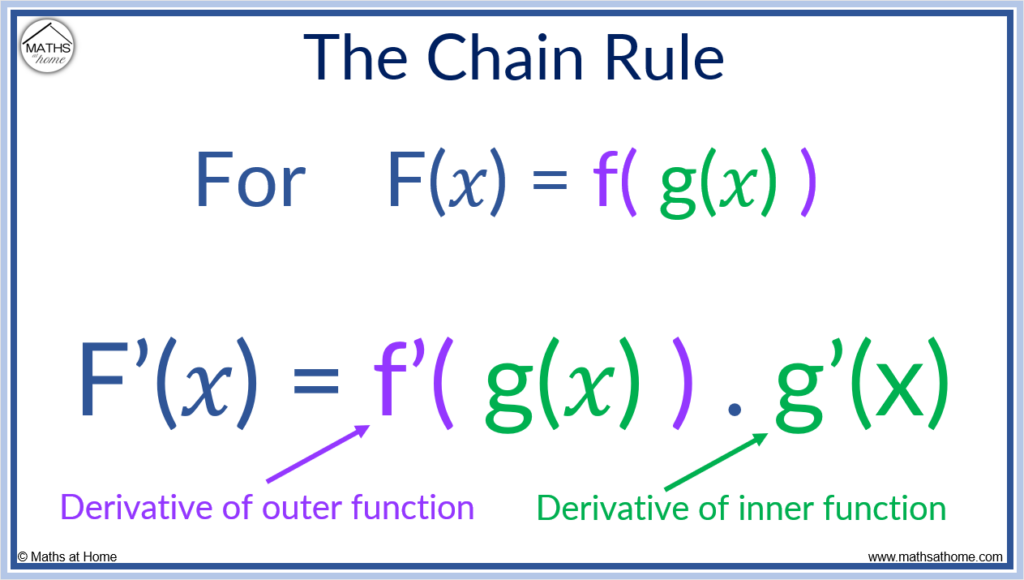
The chain rule is used when a function is within another function.
The chain rule is defined as, where u is a function of 𝑥 ( u = g(x) ) and y is a function of u ( y = f(u) ).
Alternatively, the chain rule can be written in function notation as F'(𝑥) = f'(g(𝑥)).g'(𝑥), where F(𝑥) = f(g(𝑥)). g(𝑥) is the inner function and f(𝑥) is the outer function.
In words, the chain rule requires finding the derivative of the outer function while keeping the inner function the same and then multiplying this by the derivative of the inner function.
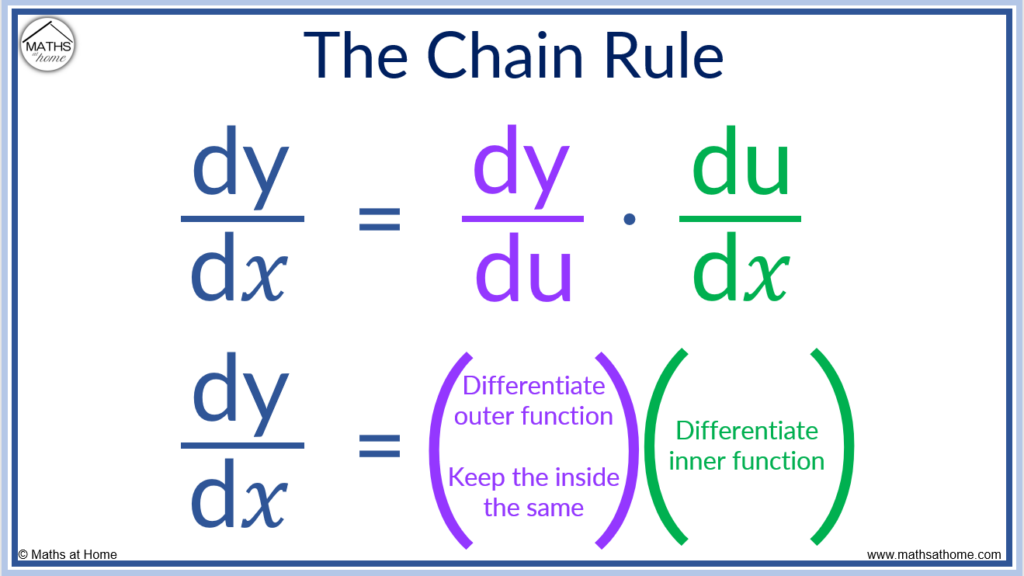
To use the chain rule, the following rules are required:
- The function must be a composite function of two or more functions
- Such functions must be differentiable themselves
How to Do the Chain Rule
To do the chain rule:- Differentiate the outer function, keeping the inner function the same.
- Multiply this by the derivative of the inner function.
For example, differentiate (4𝑥 – 3)5 using the chain rule
In this example we will use the chain rule step-by-step. Below this, we will use the chain rule formula method.
We define 4𝑥 – 3 as the inner function and the ( )5 as the outer function.
Step 1. Differentiate the outer function, keeping the inner function the same
The outer function is the ( )5. We differentiate this like we would 𝑥5.
𝑥5 would differentiate to 5𝑥4 and so we write ( )5 differentiated as 5( )4.
We keep the inner function of 4𝑥-3 the same, so we write 5(4𝑥 – 3)4.
However because we have 4𝑥 – 3 inside the brackets and not just 𝑥, we must also include step 2.
Step 2. Multiply this by the derivative of the inner function
From step 1. we already have 5(4𝑥 – 3)4 and now we must multiply this by the derivative of the inner function.
The inner function is the function inside the brackets. It is 4𝑥 – 3.
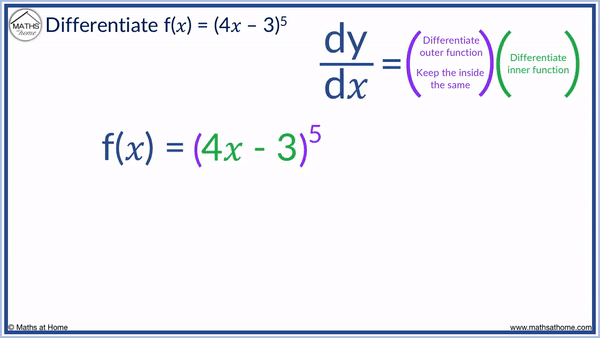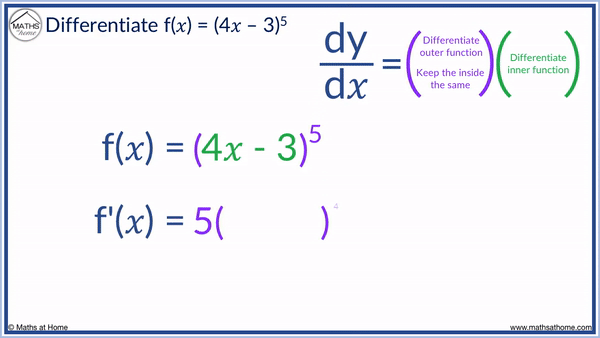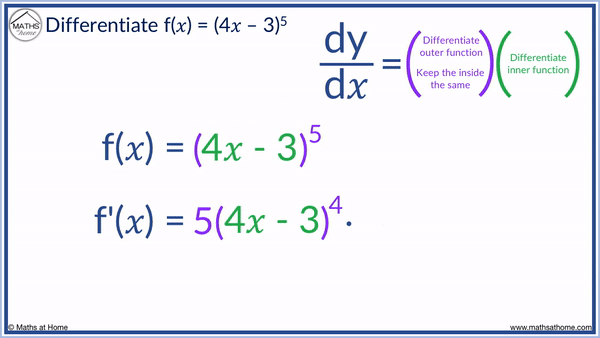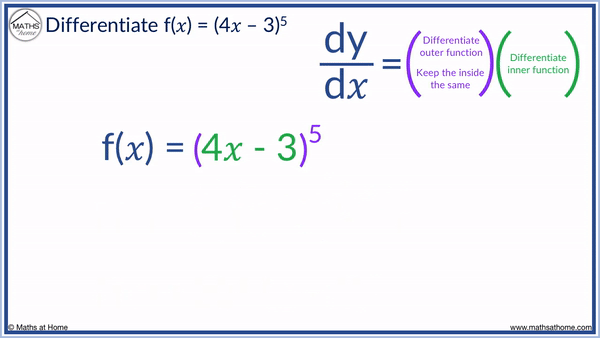
We differentiate 4𝑥 – 3 to get 4. So we must multiply the result of 5(4𝑥 – 3)4 by 4.
We arrive at the answer of f'(𝑥) = 20(4𝑥 – 3)4.
We will now use the chain rule formula to differentiate this function. The answer will be the same.
The chain rule formula states that F'(𝑥) = f'(g(𝑥).g'(𝑥), where g(𝑥) is the inner function and f(𝑥) is the outer function.
Therefore for F(𝑥) = (4𝑥 – 3)5, g(𝑥) = 4𝑥 – 3 and f(𝑥) = 𝑥5.
f'(𝑥) is therefore 5𝑥4.
f'(g(𝑥)) means to substitute g(𝑥) in place of 𝑥 in f'(𝑥).
Therefore f'(g(𝑥)) = 5(4𝑥 – 3)4.
g'(𝑥) = 4.
Therefore F'(𝑥) = f'(g(𝑥).g'(𝑥) becomes F'(𝑥) = 5(4𝑥 – 3)4 × 4.
This simplifies to F'(𝑥) = 20(4𝑥 – 3)4.
The Chain Rule with Trigonometry
The chain rule is used to differentiate trigonometric functions containing another function. Differentiate the trigonometric function, keeping the inner function the same and then multiply this by the derivative of the inner function.
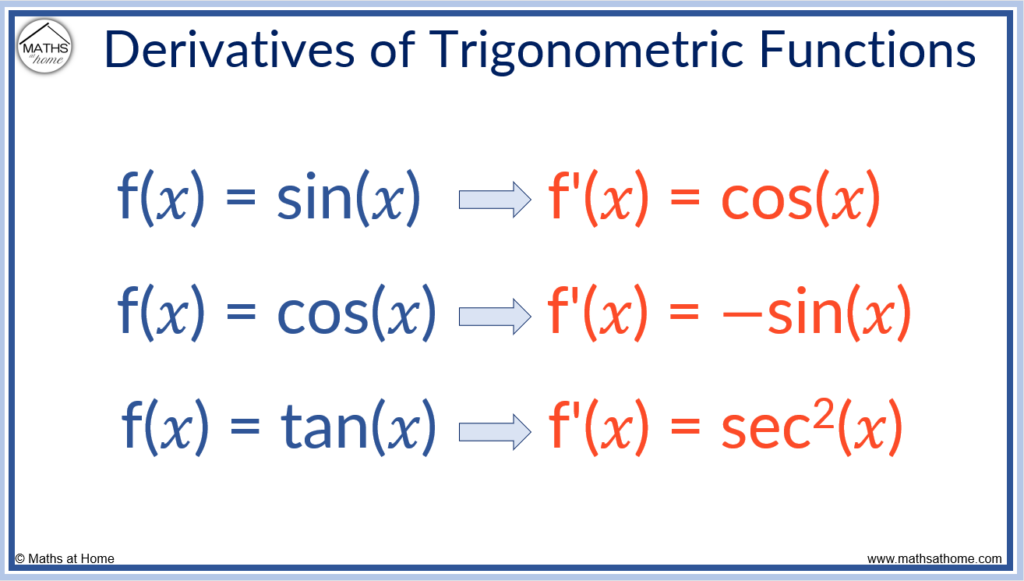
The following rules for differentiating the trigonometric functions of sin(𝑥), cos(𝑥) and tan(𝑥) may be useful here:
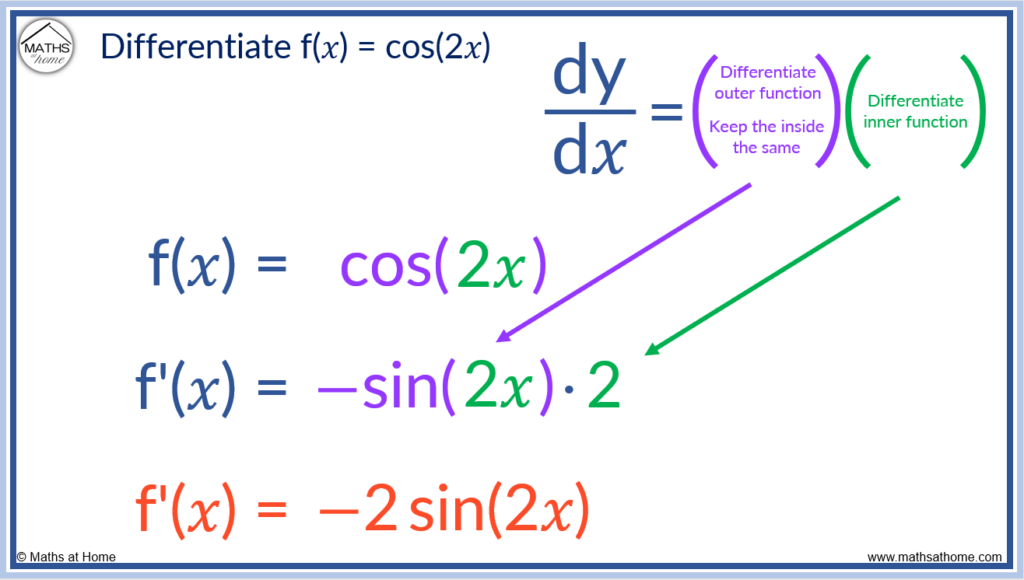
For example, differentiate cos(2𝑥) using the chain rule
cos(2𝑥) can be written as an inner function of 2𝑥 and an outer function of cos().
Step 1. Differentiate the outer function, keeping the inner function the same
cos(𝑥) differentiates to -sin(𝑥) and so, keeping the inner function as 2𝑥 rather than 𝑥, we get -sin(2𝑥).
Step 2. Multiply this by the derivative of the inner function
The inner function is 2𝑥 and its derivative is 2.
We multiply -sin(2𝑥) by 2 to get f'(x) = -2sin(2𝑥).
- Write the trigonometric function as the inner function in brackets and the power as the outer function.
- Bring down the power and subtract one from the power, keeping the trigonometric function inside the same.
- Multiply this by the derivative of the trigonometric function.
For example, differentiate sin4(2𝑥) using the chain rule
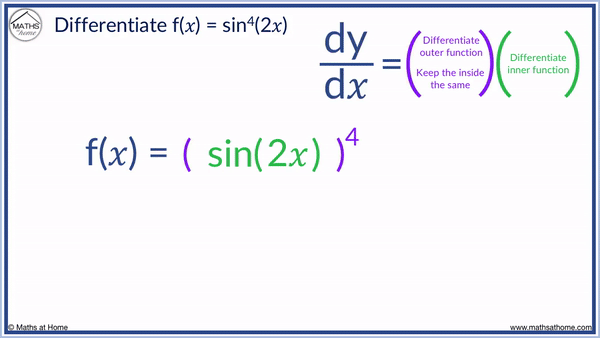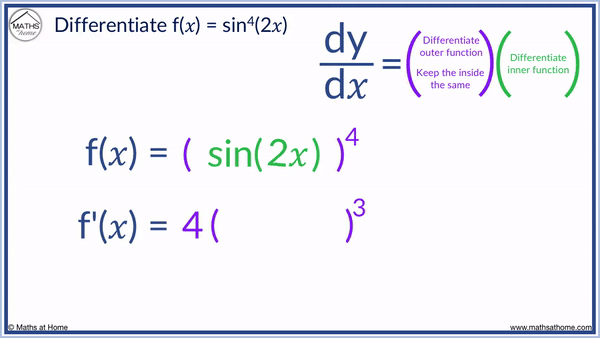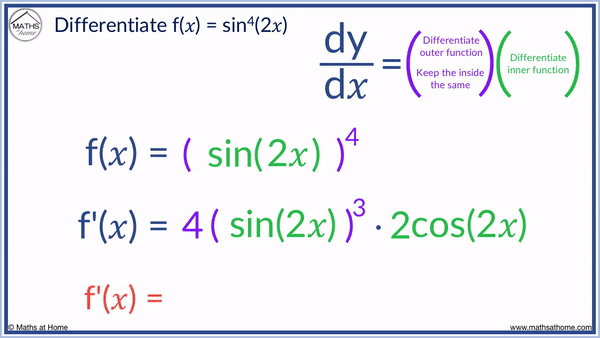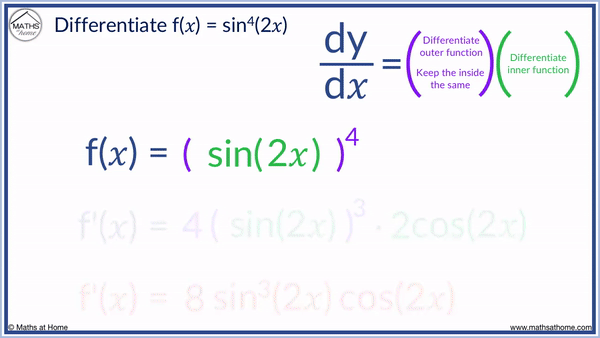
Step 1. First write sin4(2𝑥) as [ sin(2𝑥) ]4.
Step 2. Bring down the power and subtract one from the power, keeping the trigonometric function the same.
We bring down the 4 in front of the brackets, the power becomes 3 and we keep sin(2𝑥) inside the brackets, which gives us 4[ sin(2𝑥) ]3.
Step 3. Multiply by the derivative of sin(2𝑥). We use the chain rule here, so sin(𝑥) is the outer function which differentiates to cos(𝑥).
We keep the 2𝑥 inside so we get cos(2𝑥). We then multiply this by the derivative of 2𝑥, which is 2.
sin(2𝑥) differentiated is 2cos(2𝑥).
So we multiply 4[ sin(2𝑥) ]3 by 2cos(2𝑥).
f'(𝑥) = 8sin3(2𝑥)cos(2𝑥)
The Chain Rule with Logs
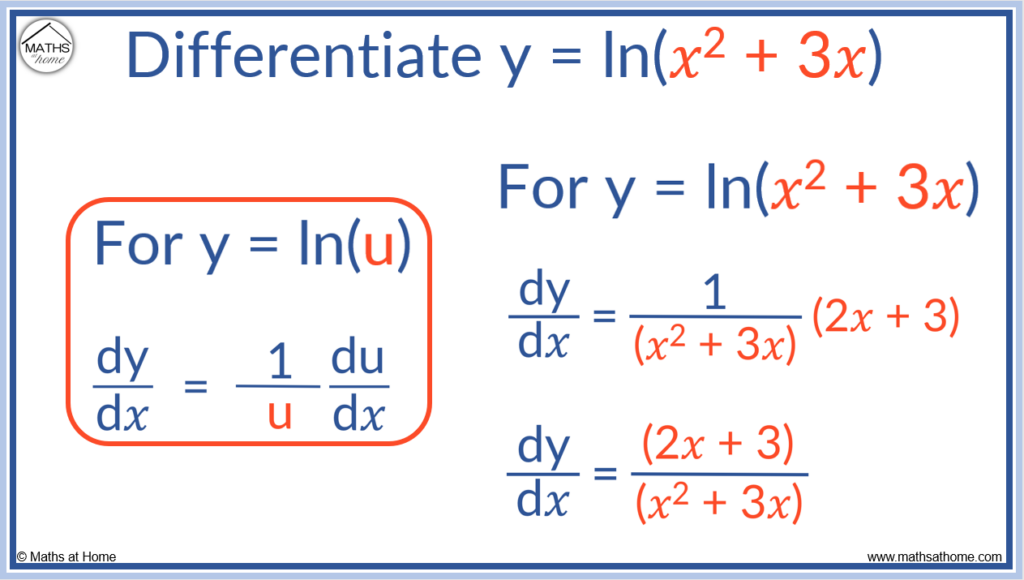
The chain rule states that for y = ln(u), dy/d𝑥 = 1/u × du/d𝑥. In words, differentiate the inner function and then divide this by the inner function. For example if y = ln(𝑥2 + 3𝑥), dy/d𝑥 = (2𝑥 + 3)/(𝑥2 + 3𝑥).
The derivative of y = ln(u) is 1/u × du/d𝑥.
u is the function inside the ln function. For y = ln(𝑥2 + 3𝑥), u = 𝑥2 + 3𝑥.
Therefore du/d𝑥 = 2𝑥 + 3.
The derivative dy/d𝑥 =.
We can write this as
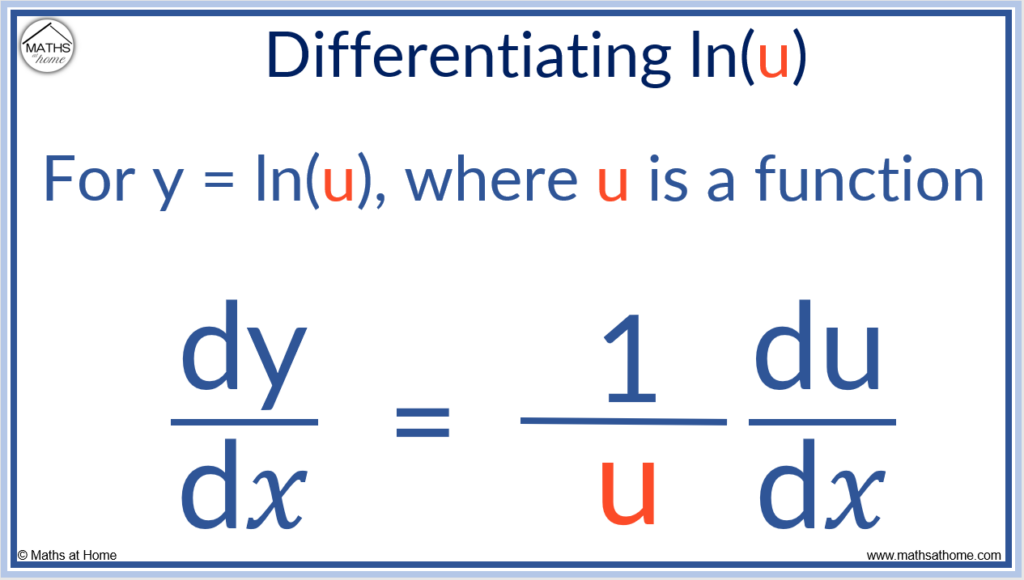
The chain rule allows us to differentiate log functions. The derivative of y = ln( f(𝑥) ) can be written as:
or .
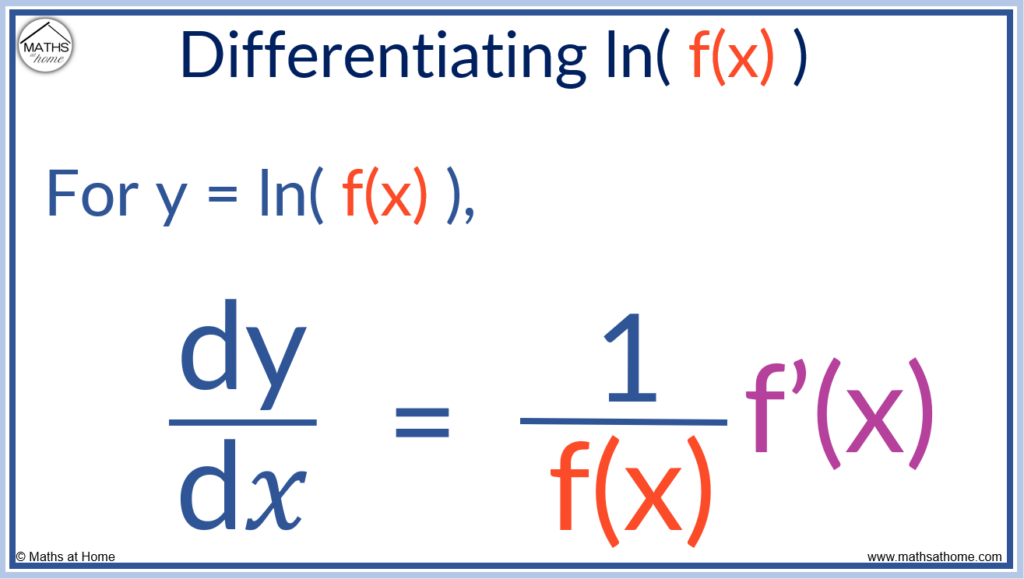
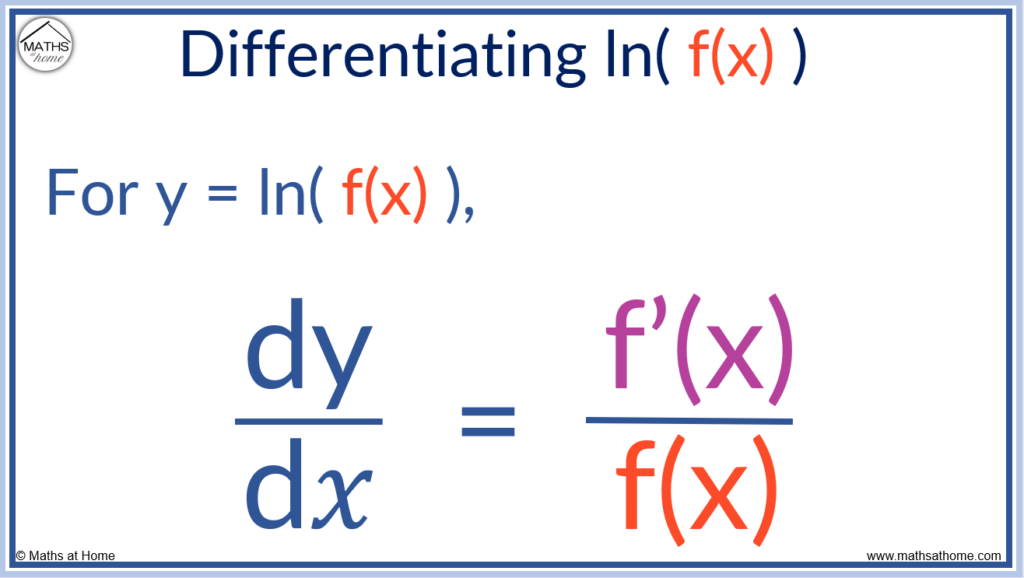
To differentiate log of any base, if y = logaf(𝑥) then .
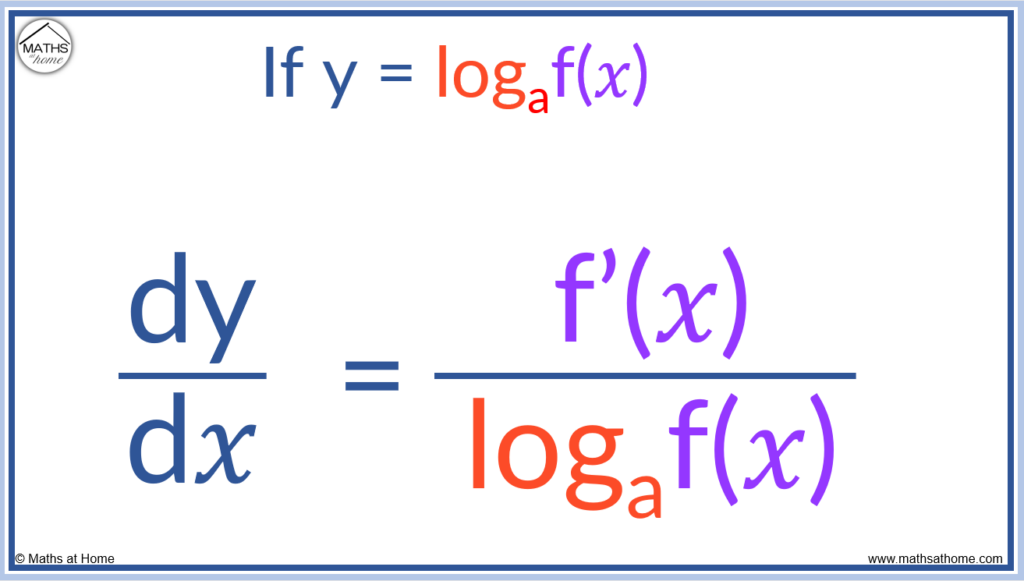
For example, differentiate y = log5(2𝑥 + 1):
Here f(𝑥) = 2𝑥 + 1 and so, f'(𝑥) = 2.
Substituting these into the formula, we get:
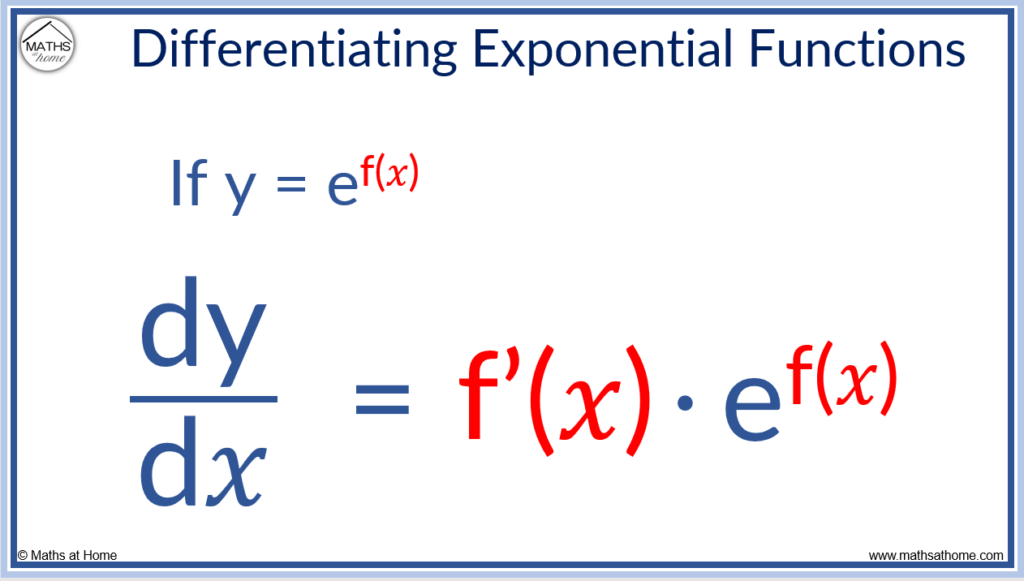
The Chain Rule with Exponential Functions
The derivative of y = e𝑥 is dy/d𝑥 = e𝑥 and so using the chain rule, the derivative of y = ef(𝑥) is dy/d𝑥 = f'(𝑥).ef(𝑥). Simply differentiate the power of e and multiply this by the original function.
For example, differentiate e5𝑥+3.
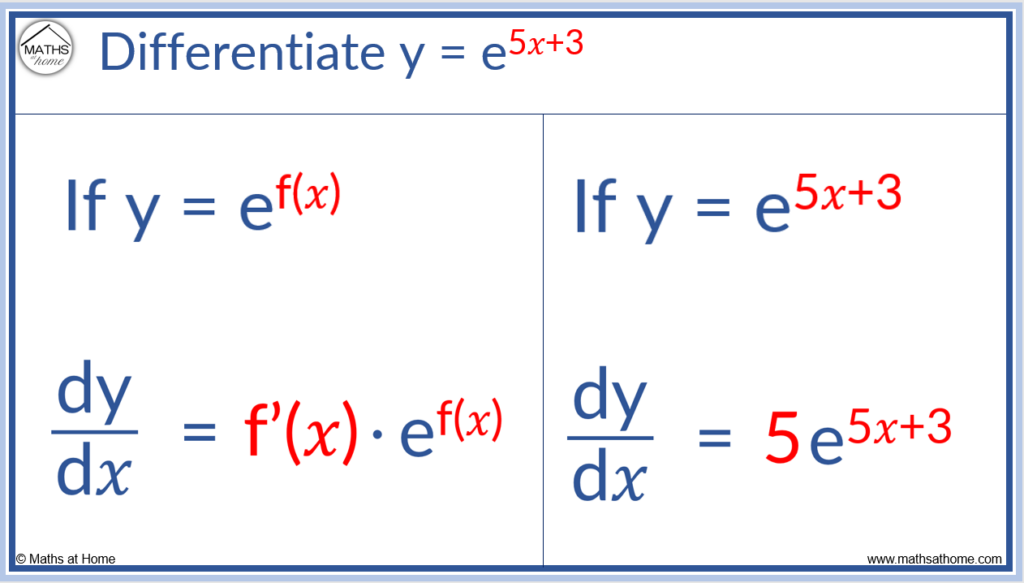
In this example, f(𝑥) = 5𝑥 + 3 and so, f'(𝑥) = 5.
To find the derivative of y = e5𝑥+3 , we simply multiply it by 5.
We get dy/d𝑥 = 5 e5𝑥+3.
Applying the Chain Rule with Three Functions
The chain rule can be applied to the composition of three functions. If y(𝑥) = h(g(f(x))), then y'(𝑥) = f'(𝑥) . g'(f(𝑥)) . h'(g(f(𝑥))). However, it is easier to apply the chain rule twice to differentiate three functions.
For example, differentiate f(𝑥) = sin2(5𝑥).
Here we have the composition of 3 functions.
- The innermost function is 5𝑥.
- Acting on the 5𝑥 is the sin function
- Finally, the sin function is raised to the power of 2
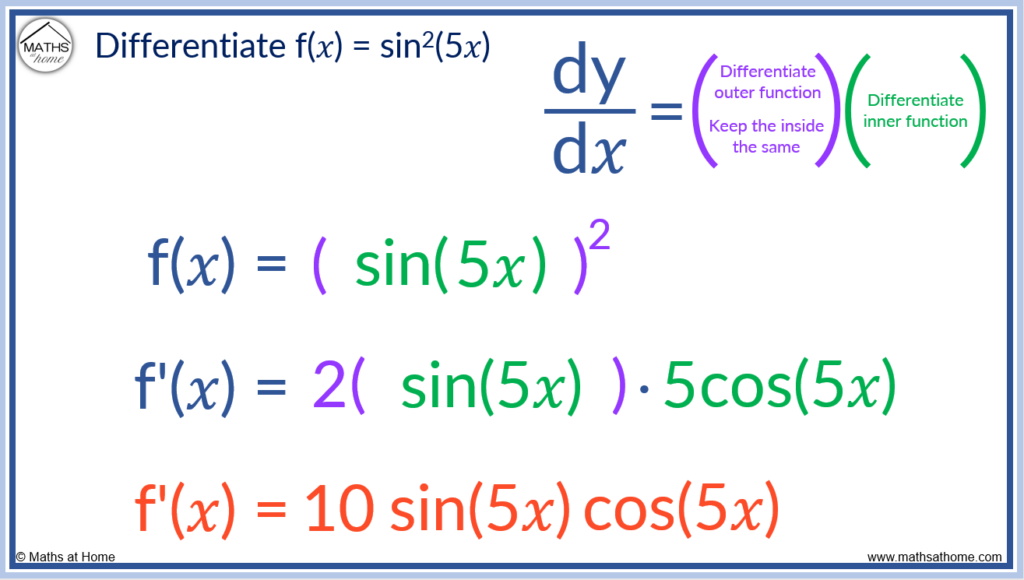
We write sin2(5𝑥) as [ sin(5𝑥) ]2.
We differentiate using the chain rule, so that we differentiate the outer function, keeping its inner function the same and then multiply by the derivative of the inner function.
Differentiating the outer squared function, keeping the inner function the same we have 2[ sin(5𝑥) ]. The power 2 came down, we subtracted 1 from the power and we kept the sin(5𝑥) on the inside the same.
We now need to multiply this by the derivative of the inner function, sin(5𝑥). This requires the chain rule to be used for a second time.
We differentiate the outer function of sin to get cos and we keep the inner function of 5𝑥 the same. We get cos(5𝑥). We need to multiply this by the derivative of the inner function, 5𝑥. We find the derivative of sin(5𝑥) is 5cos(5𝑥).
We now multiply the previous result of 2[ sin(5𝑥) ] by 5cos(5𝑥) to get the final derivative of 10sin(5𝑥)cos(5𝑥).
Chain Rule Examples with Solutions
Here are some examples of using the chain rule to differentiate a variety of functions:
| Function | Calculation | Derivative |
| f(𝑥) = (5𝑥 + 1)3 | 3 × (5𝑥 + 1)2 × 5 | f'(𝑥) = 15(5𝑥 + 1)2 |
| f(𝑥) = sin(5𝑥) | cos(5𝑥) × 5 | f'(𝑥) = 5cos(5𝑥) |
| f(𝑥) = cos(10𝑥) | -sin(10𝑥) × 10 | f'(𝑥) = -10sin(10𝑥) |
| f(𝑥) = -3tan(2𝑥) | -3sec2(2𝑥) × 2 | f'(𝑥) = -6 sec2(2𝑥) |
| f(𝑥) = 10e4𝑥 | 10e4𝑥 × 4 | f'(𝑥) = 40e4𝑥 |
| f(𝑥) = ln(𝑥3) | 1/(𝑥3) × 3𝑥2 = (3𝑥2)/(𝑥3) | f'(𝑥) = 3/𝑥 |
When to Use the Chain Rule
The chain rule is used to differentiate any composite function of the form y = f(g(𝑥)). That is a function that has an inner function with an outer function applied to it. For example y = (3𝑥 + 2)5 is made of the functions g(𝑥) = 3𝑥 + 2 and f(𝑥) = 𝑥5.
Here are some example of when and when not to use the chain rule:
| Example | Should I use the chain rule? | Why? |
| y = (3𝑥+2)5 | Yes | The inner function is 3𝑥+2 and the outer function is 𝑥5. |
| y = 𝑥5 | No | There is only one function 𝑥5. It can be differentiated directly. |
| y = (𝑥+3) sin(𝑥) | No | It is the product of two functions. Use the product rule. |
| y = sin(2𝑥+1) | Yes | The inner function is 2𝑥+1 and the outer function is sin(𝑥) |
| y = (𝑥+5)/(3x+5) | No | It is a fraction with a function for a numerator and denominator. Use the quotient rule. |
| y = ln(𝑥4-𝑥) | Yes | The inner function is 𝑥4-𝑥. The outer function is ln(𝑥). |
| y = e2𝑥 | Yes | The inner function is 2𝑥 and the outer function is e𝑥. |
Chain Rule Proof
To prove the chain rule, consider dy/dx as a limit of Δy/Δ𝑥 as 𝑥 tends to zero. This can be written as limits of Δy/Δu × Δu/Δ𝑥. Evaluating these limits as 𝑥 and u tend to zero, we derive the chain rule as dy/d𝑥 = dy/du × dy/d𝑥.
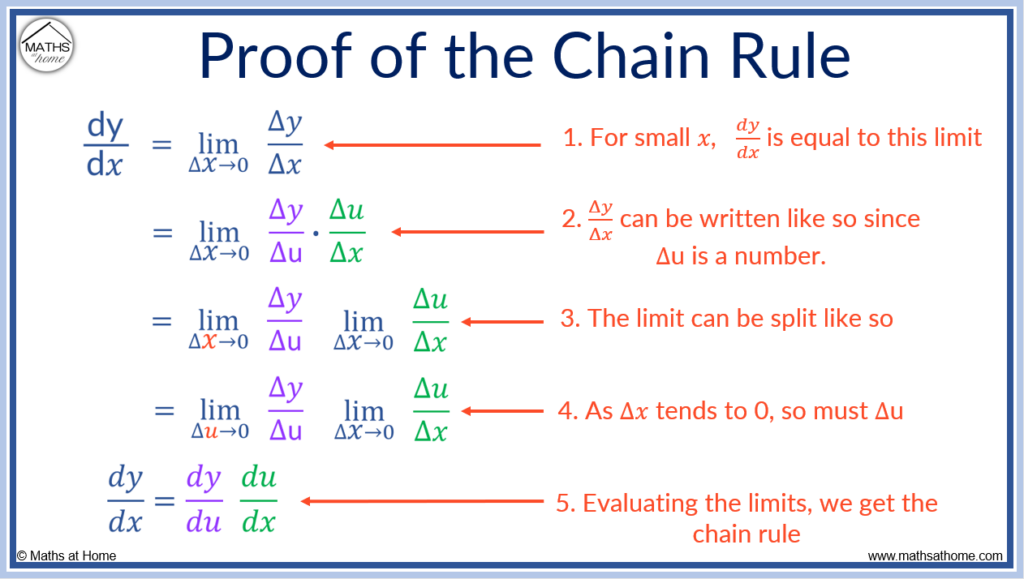
To prove the chain rule:
- Write dy/d𝑥 as a limit of Δy/Δ𝑥 as 𝑥 tends to zero.
- Write the limit of Δy/Δ𝑥 as Δy/Δu × Δu/Δ𝑥. Δu is just a number so this can be done.
- Separate the limit into 2 limits of Δy/Δu and Δu/Δ𝑥.
- As Δ𝑥 tends to 0, so does Δu.
- Evaluate both limits to get dy/d𝑥 = dy/du × du/d𝑥.
